-
Call Us +91-7086689050
-
Get In Touch info@growthfarmtechnologies.com
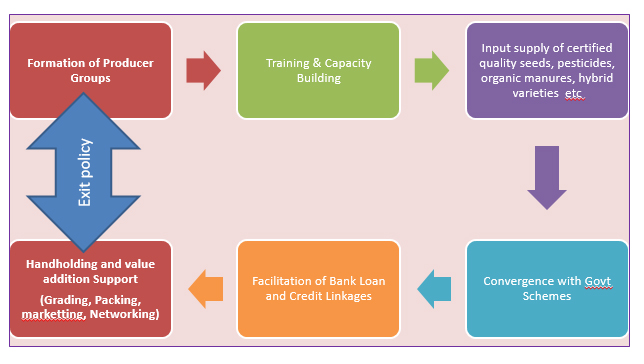
Training and capacity building of farmers through farm mechanization
and innovative agricultural techniques
Arable crop production in dried areas of Northern India
In various farming areas, due to lack of rainfall and prevailing Anna Pratha the farmers in general take only one crop. During field visit it was found that most of the villages of Assam and UP nearby to the waterbody have started taking two crops by using the collected water for irrigation. Besides providing water for irrigation in agricultural fields, the collected water has improved the water level in the village wells in most of the areas. During field visits and post trainings at most of the sites the villagers were happy and said that their agriculture income has increased, almost doubled, due to availability of water. The availability of water also gives life to their cattle as earlier during acute summer their cattle used to roam here and there in search of water. Synergies of forest, wasteland, non-arable, arable land, rearing of animals, micro-enterprising, has thus been optimized in the watershed management programme. The increasing income of farmers having agricultural land near by structures is one of the aspects of the initiatives Beside this, some of the other benefits as observed during field visit are given below:
Methods to be adopted:
Soil and moisture conservation measures have not only helped in regeneration of native trees spp but have also promoted regeneration of many natural grasses and legume species which otherwise would have been lost due to continuous removal of top soil. The growth in bonanali and good coppicing in existing root stock not only make the areas green but even fulfil the forage demand of the locals. The survival of planted plants is also quite good. The good growth of quality grasses of rangeland i.e. Dicanthimum annulatum, Sehima nervosum and Chrysopogon fulvus was observed at some sites. It is a good indicator for more forage production in future. It can provide good cash benefits to the farmers and can create ample scope for food, fodder and firewood in the villages and thus thereby enhance their livelihood options..
Soil Fertility: Greening of degraded lands makes the degraded areas full of humus resulting in soil fertility build-up over the years.
The impact of mechanical and vegetational conservation measures are now seeming to be good in most of the areas where regeneration of local tree species initiated as well as greening of ground cover, initiated in the periphery of the structures. The seed sowing of leguminous grasses and other fodder species along the Bonanali and re-generation of native species will ensure the fodder availability in the area. It will give a boost to the pastoral economy.
The increase in green cover and creating water bodies have not only improved the ecology of the areas but also have paved a way for improving the faunal population. The chirping of birds has become quite common near the water bodies and the same was observed during the field visit. The frontline officers informed that the population of eagle, hawk peacock, kingfisher, sunbirds etc has increased in a good numbers.
It has improved the rain water conservation by increasing the water aquifers, trenches, plantation of indigeneous fruits, shrubs thereby improving functions and community services of forest land. Geo hydrological situations has been improved by open dug wells.